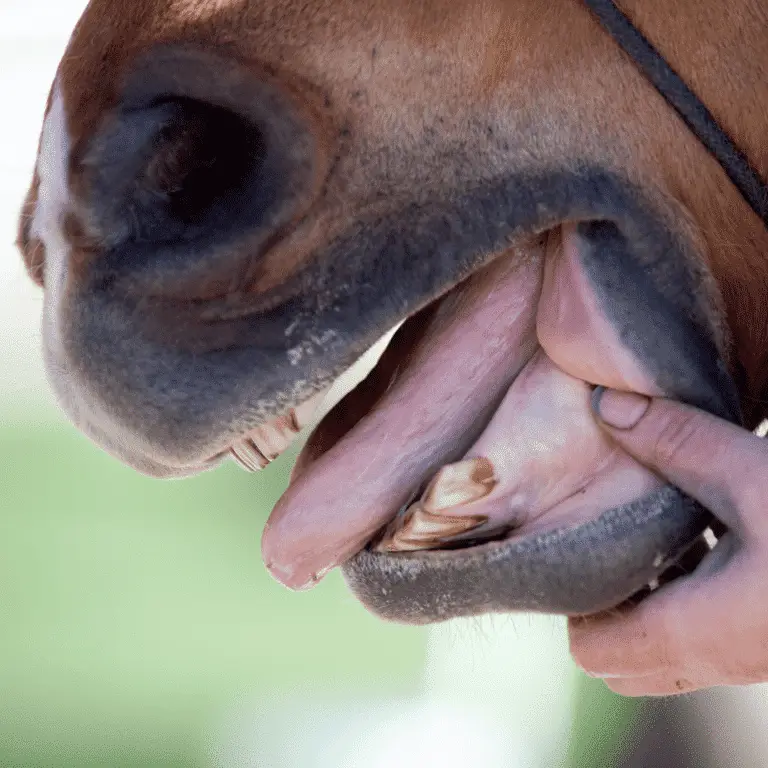

Equine malocclusion in Horses
Equine Malocclusion in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Malocclusion in horses is a faulty alignment between
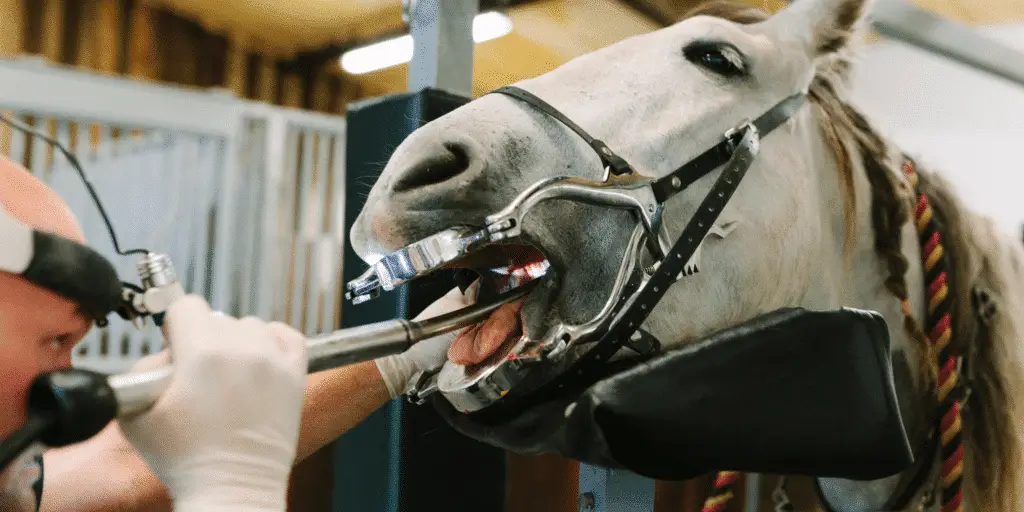

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
The treatment for equine dental hooks (a common issue in horse’s teeth) depends on the severity and location of the hook, but it typically involves removing the hook through a process called “floating”. This is done by using a specialized tool called a “float” to reshape the tooth and remove the hook. In some cases, dental surgery may be necessary if the hook is very deep or affecting the horse’s ability to chew and eat. Pain management, antibiotics, and proper aftercare are also important components of treatment. It is always recommended to consult a veterinarian experienced in equine dentistry for proper diagnosis and treatment.
There are several steps you can take to prevent the formation of dental hooks in horses:
Regular dental exams and floating: Regular dental exams by a veterinarian experienced in equine dentistry, as well as timely and appropriate floating, can help prevent hooks from forming and keep your horse’s teeth healthy.
Proper diet: Providing a balanced diet with adequate forage (hay or pasture) and limited concentrates (grains) can help prevent the overgrowth of teeth, which can lead to hooks.
Avoiding improper bit use: Using proper bits and avoiding bits that apply too much pressure to the horse’s mouth can help prevent dental issues, including hooks.
Monitoring your horse’s behavior: Observing your horse’s behavior, such as changes in eating habits or excessive salivation, can indicate the presence of dental problems, including hooks.
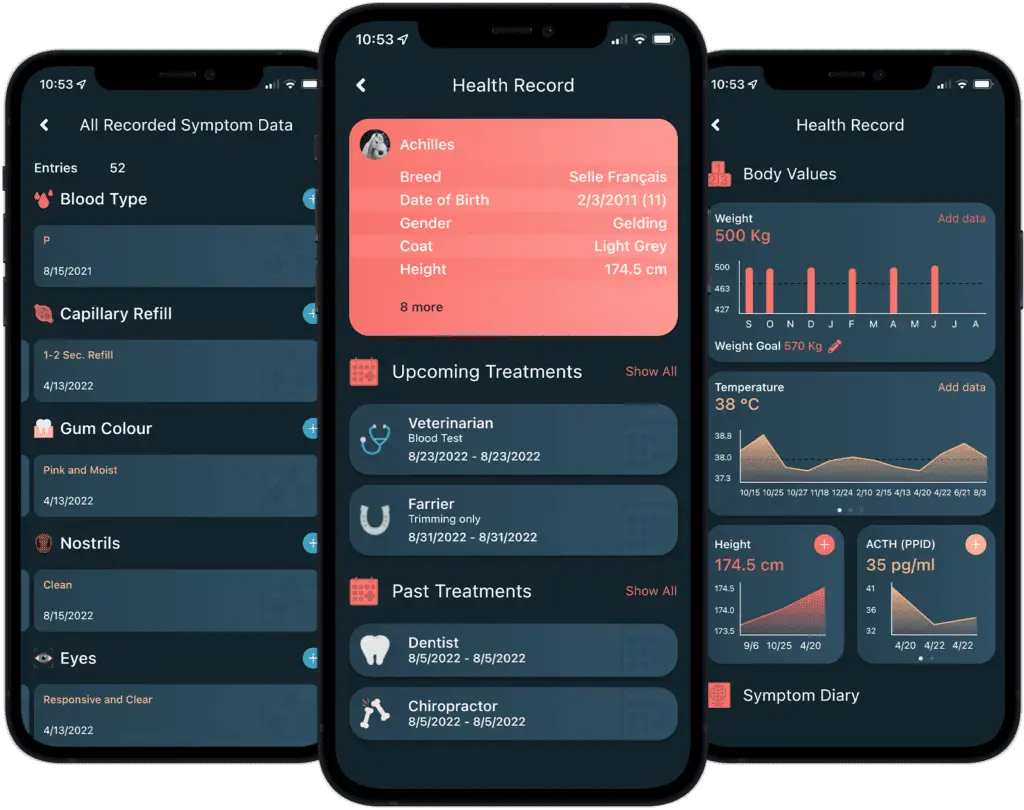
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Equine Malocclusion in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Malocclusion in horses is a faulty alignment between
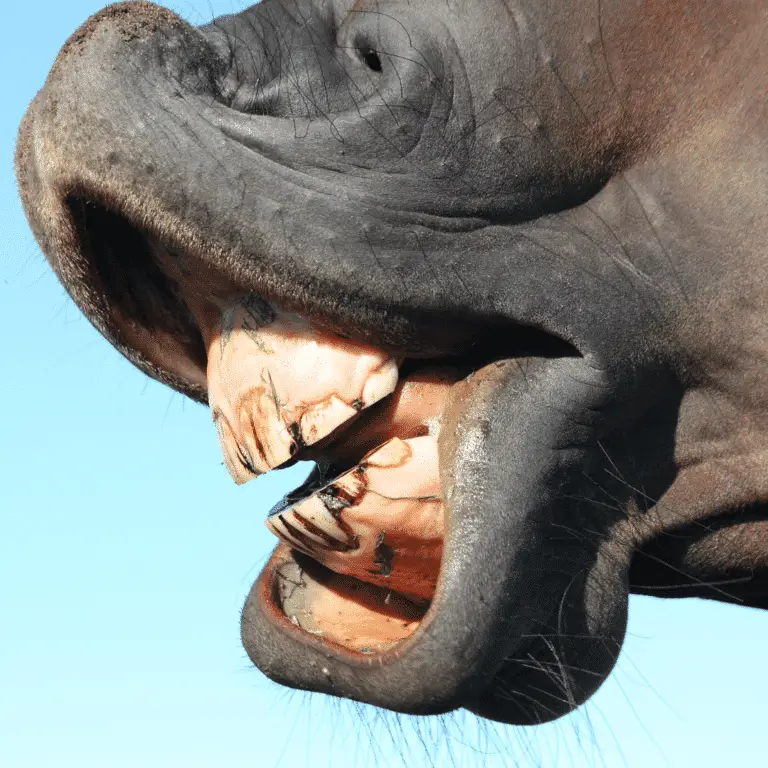

Wave Mouth in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Wave mouth is a dental condition commonly seen
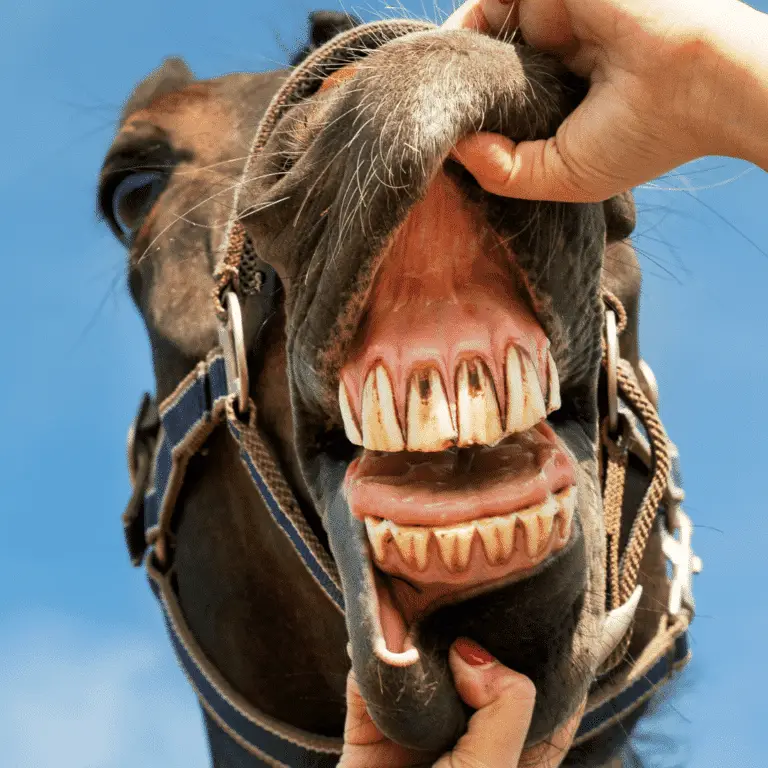

EOTRH Syndrome in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Equine Odontoclastic Tooth Resorption and Hypercementosis, also known