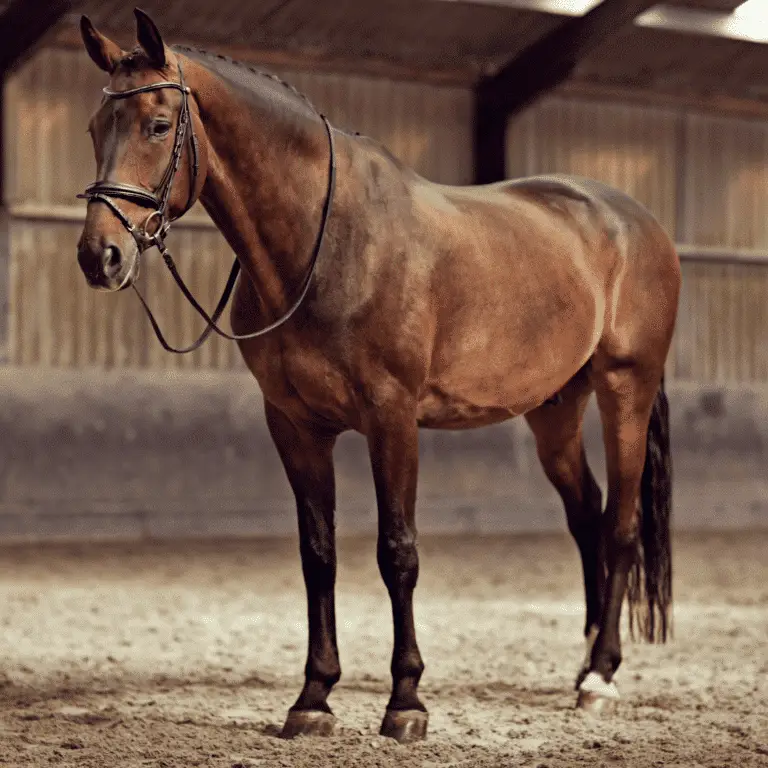

Sarcocystis Myositis
Sarcocystis Myositis in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Sarcocystis myositis is a disease in horses caused

This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly.
There is no treatment for GBED. Early recognition and euthanasia can save considerable expense for owners of foals in neonatal intensive-care units. It is important that veterinarians and breeders recognize that GBED may present both as foals born alive that subsequently succumb to GBED as well as abortion.
A DNA test is available to detect the gene mutation responsible for glycogen branching enzyme deficiency. It will identify horses that are homozygous affected, heterozygous carriers or unaffected (normal).
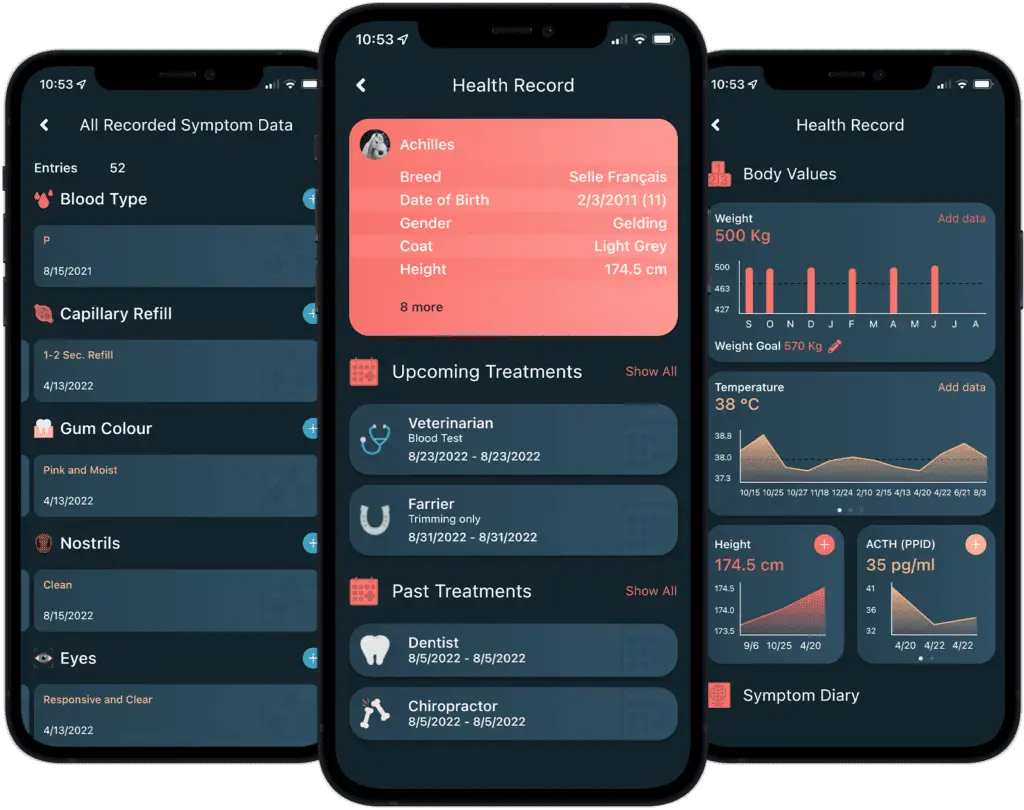
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Sarcocystis Myositis in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Sarcocystis myositis is a disease in horses caused
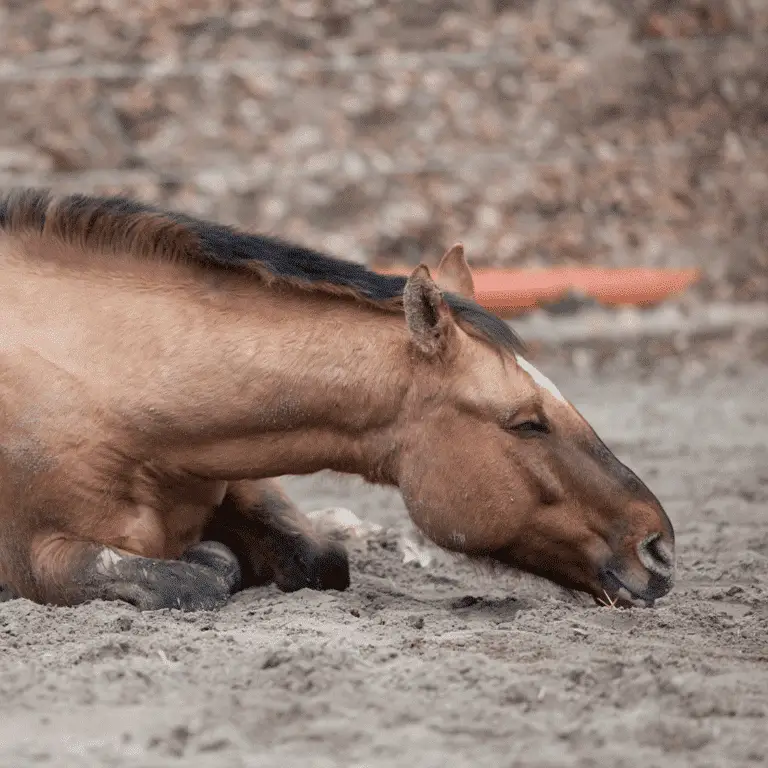

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
Anaplasma rhabdomyolysis is a muscle disease in horses caused by Anaplasma bacteria, leading to muscle damage, stiffness, and weakness, often requiring veterinary intervention.
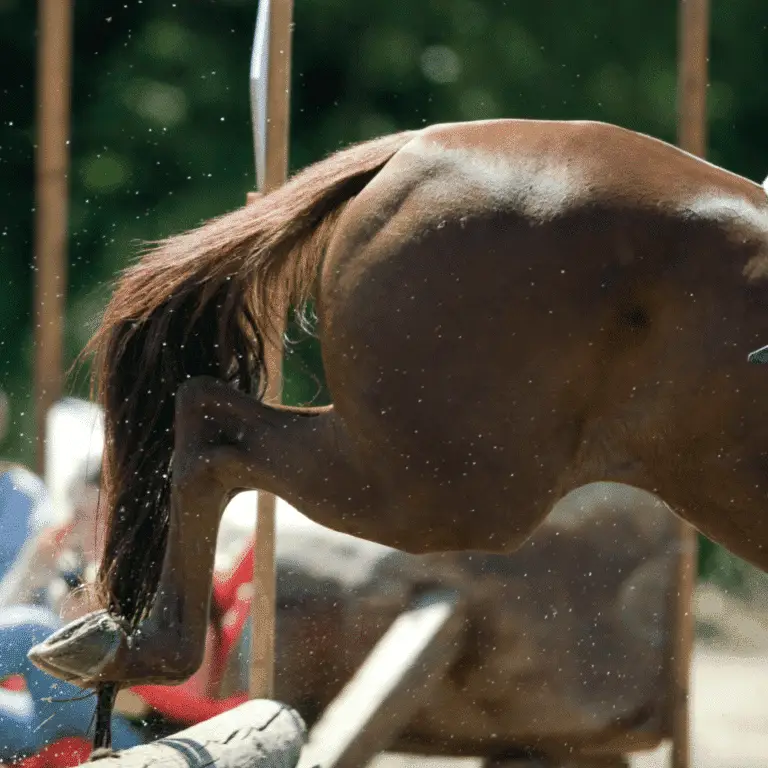

Fibrotic Myopathy in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease Fibrotic myopathy is a mechanical lameness of the