
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis in the horse and

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
Capped elbow (olecranoid bursitis) is acquired and associated with a cosmetic blemish. It is caused by trauma, usually from the shoe on the affected leg contacting the elbow during motion or when the horse is lying down.
The first course of action in providing treatment for a capped elbow is to eliminate the known causes of the trauma by reviewing the state of the horse’s shoeing and providing padded leg wraps and pads to the pastern to diminish the chances of injuries.
Trailers and stalls may need to be modified to limit the chances of contact with surfaces that can cause trauma to the horse’s elbow or hock.
Cold hydrotherapy is often recommended to reduce swelling and relieve any pain. The bursa may also be reduced in size by laser therapy or extracorporeal shock wave therapy.
Older encapsulated bursae are more refractory. Surgical treatment, where the area is opened and drained, removing fibrous tissue, is recommended for advanced chronic cases or for those that become infected.
The best preventative measures for capped elbow are monitoring limbs for abnormal swelling daily, if your horse develops a small swelling at the point of the elbow, call your vet so treatment can be considered while the swelling is still small. Stall with a thick layer of dry bedding for a cushion should your horse prefer to lie down. One other method to prevent the bursa from enlarging is to place a doughnut-shaped object called a shoe boil roll on the horse’s pastern to prevent the heel from touching the elbow as the horse lies down.
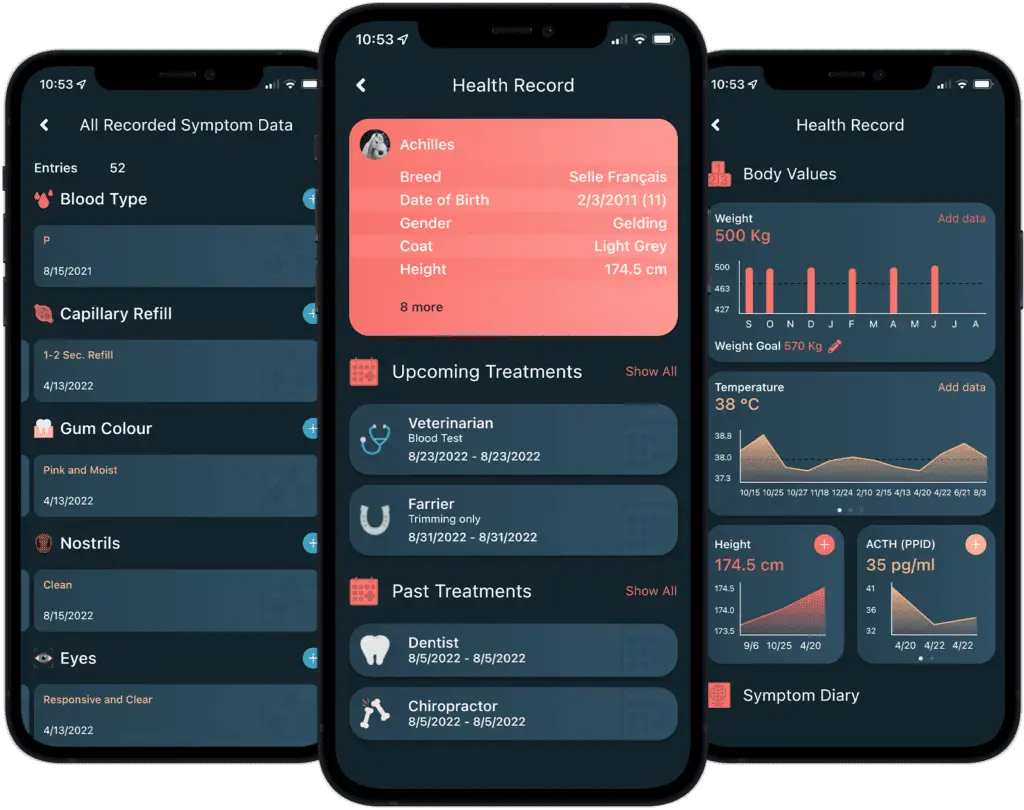
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Osteoarthritis in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis in the horse and
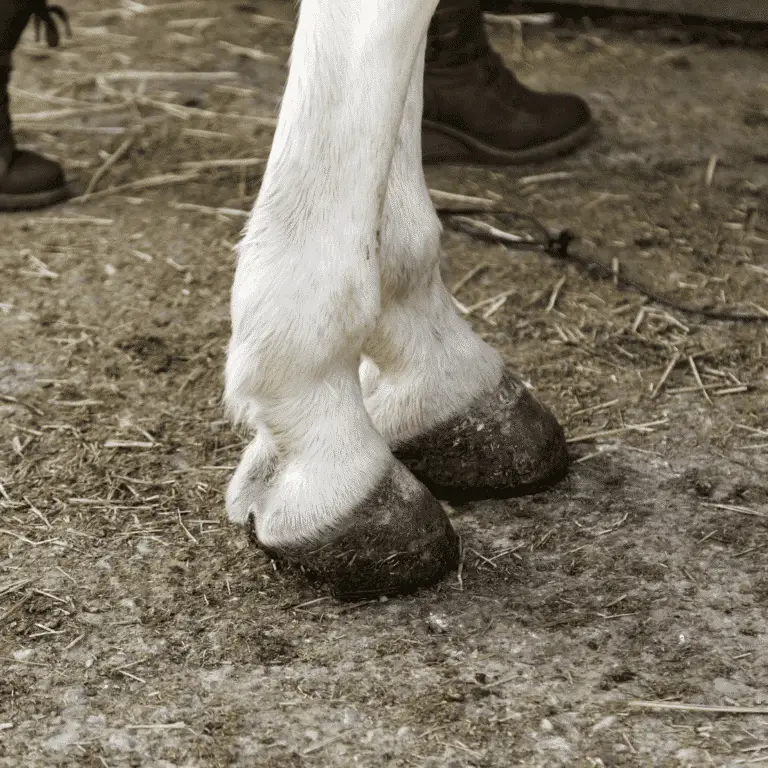
Tenosynovitis in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment Tenosynovitis refers to inflammation of the synovial membrane and the

Traumatic Arthritis in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment Traumatic arthritis (TA) which is caused by excessive/abnormal use