
Fibrotic Myopathy
Fibrotic Myopathy in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease Fibrotic myopathy is a mechanical lameness of the

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease
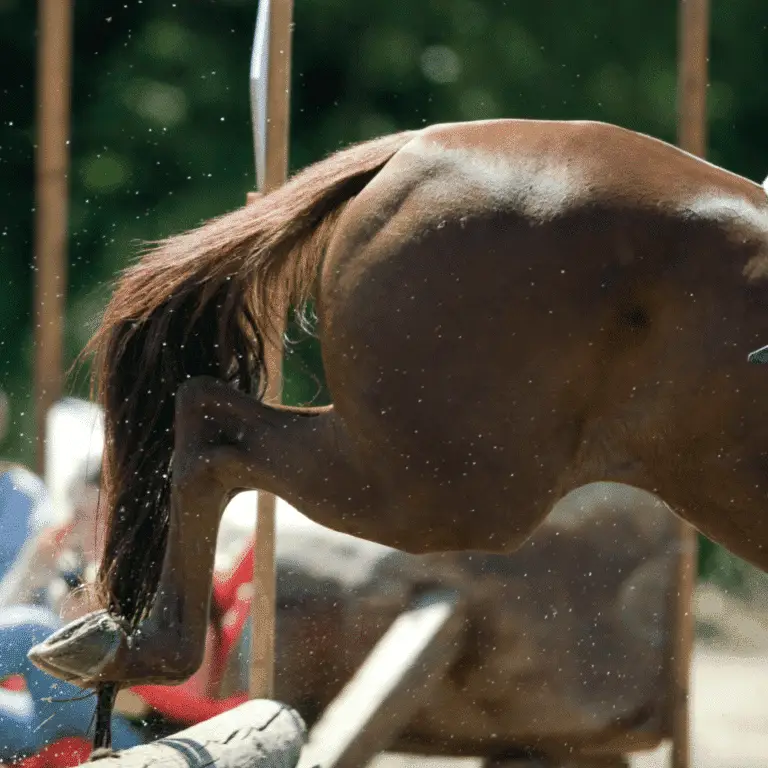
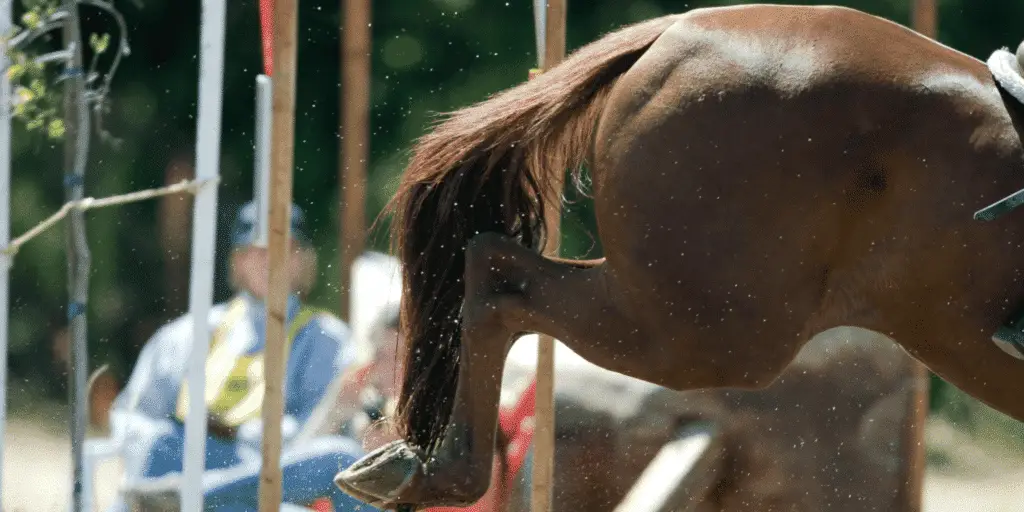
Fibrotic myopathy is a mechanical lameness of the hind limb in horses, caused by restriction of the action of the horse’s muscles. It occurs when horses injure their semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles. The gait change is caused by a mechanical limitation on movement of the hind limb and is not necessarily caused by pain.
Injury and scarring of the hamstring muscles in the upper hindquarter of the horse causes a classic change in gait with shortening of the front phase of the stride, loss of the stretchability of the normal muscle, and slapping of the foot to the ground. The injury can result from a single traumatic injury to these muscles (hyperextension injury) but can also can result from repetitive strain. In some cases, scarring can occur from repeated IM injections into the hamstring muscles.
After an acute injury, therapy should begin as soon as the horse is no longer in pain to prevent ossification (hardening) of the muscle. If your horse has local heat and inflammation, your veterinarian may prescribe an anti-inflammatory during the early stages.
Treatment plans may include hydrotherapy (cold hosing the area), stretching, alternative therapies including deep ultrasound, and heat or electric stimulation. Underwater treadmill exercises can also be beneficial once the muscle has started to heal. The aim of post-tear therapy is to regain as much normal elasticity and strength of muscle as possible, and prevent the development of excess scar tissue or fibrosis.
If a fibrotic band does occur in the muscle, there are effective surgical treatments for fibrotic myopathy. Cutting of the scar itself, or the tendon below it may be helpful to restore normal length and elasticity of the hamstring and a more normal gait. The surgery is often performed in the standing horse. Rest is advised during the early period after injury to the muscle, as the initial injury is painful. In mild cases, physical therapy and massage may be helpful, especially soon after injury
Warming up horses prior to exercise. Daily exercise or turnout. Limit intramuscular injections (and volume of substance to < 10ml) into the thigh muscles of athletic horses
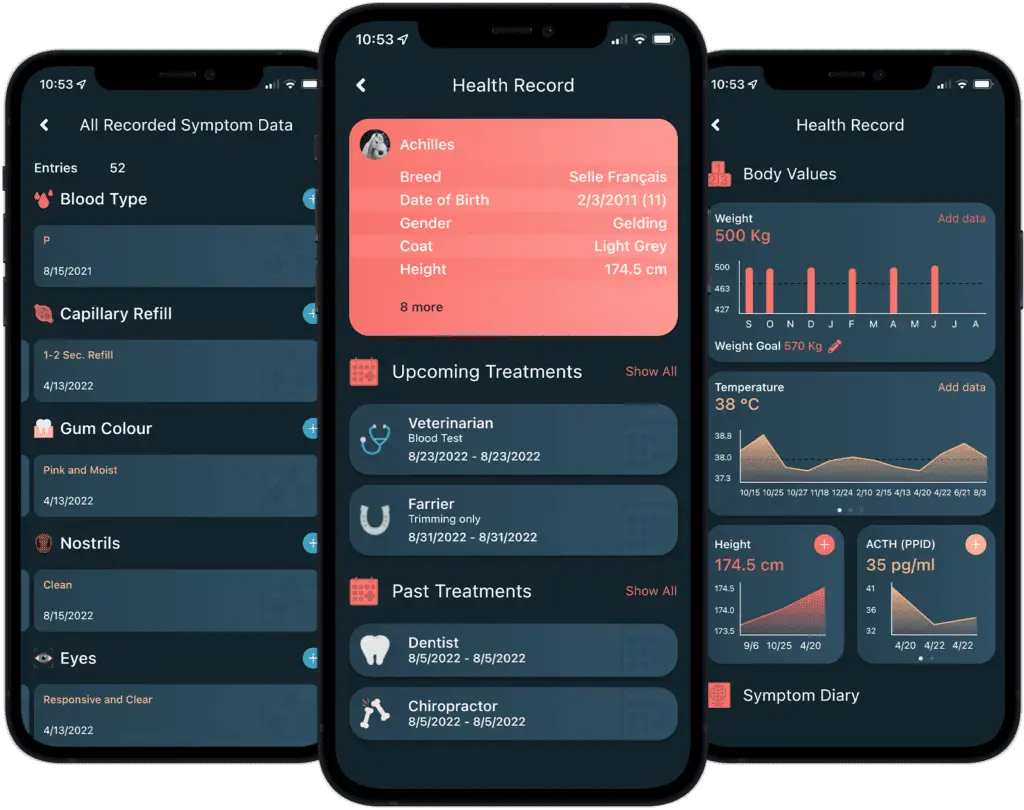
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Fibrotic Myopathy in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease Fibrotic myopathy is a mechanical lameness of the

Equine Exertional Rhabdomyolysis (Tying-Up) This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly. Equine exertional rhabdomyolysis, more

Sarcocystis Myositis in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Sarcocystis myositis is a disease in horses caused