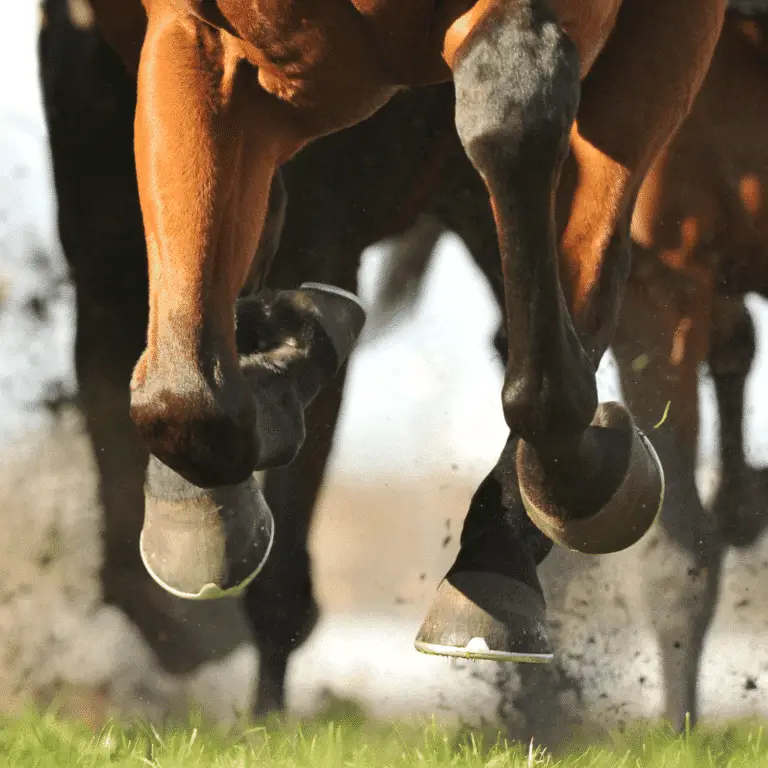

Sheared Heels
Sheared Heels in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment. Sheared heels can be defined as a hoof capsule

This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly.
Laminitis is an inflammation of the laminae, the connection of tissue between the hoof wall and the surface of the coffin bone (pedal bone). It leads to extreme pain, instability and in severe cases, a seperation between the hoof wall and bone, leadin the coffin bone to rotate.
Laminitis is commonly divided into three phases: developmental, acute, and chronic.
Developmental: The developmental phase is the beginning of the injury to the laminae. Horses typically do not show clinical signs, but the primary disease and pathological processes are underway.
Acute: During this phase, which can last hours to days, the first signs of lameness are observed. Rotation and displacement of the coffin bone may occur, but not all horses develop bone displacement. Horses may exhibit increased digital pulses, increased hoof temperatures, swelling in the limbs, constant weight shifting, subtle or obvious lameness, a stance indicating discomfort, unwillingness to move, and reluctance to rise.
Chronic: Clinical signs that last more than a week are diagnosed with chronic laminitis. During this phase, pain and lameness are caused by displacement of the coffin bone, the extent of which may be observed on radiographs. Affected horses exhibit increased digital pulses, varying degrees of lameness, and weight loss. Hooves may have a cleft at the coronary band and a characteristic “dished” appearance. Growth rings on the hooves may be noticeable in longstanding cases. Some horses develop white line separation, seedy toe and abscesses. In severe cases, the coffin bone can penetrate through the sole of the hoof.
Medical treatment for Laminitis may include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication to control pain and inflammation and a derived psychotropic drug to reduce mobility. Foot support is vital, providing a deep bed which extends to the door, frog supports attached to the feet such as Lilypads or TLC frog supports. Box rest along with dietary changes are important factors. Feed grass hay and no or minimal concentrates.
It’s important to note that once a horse has had laminitis, it may be likely to recur.
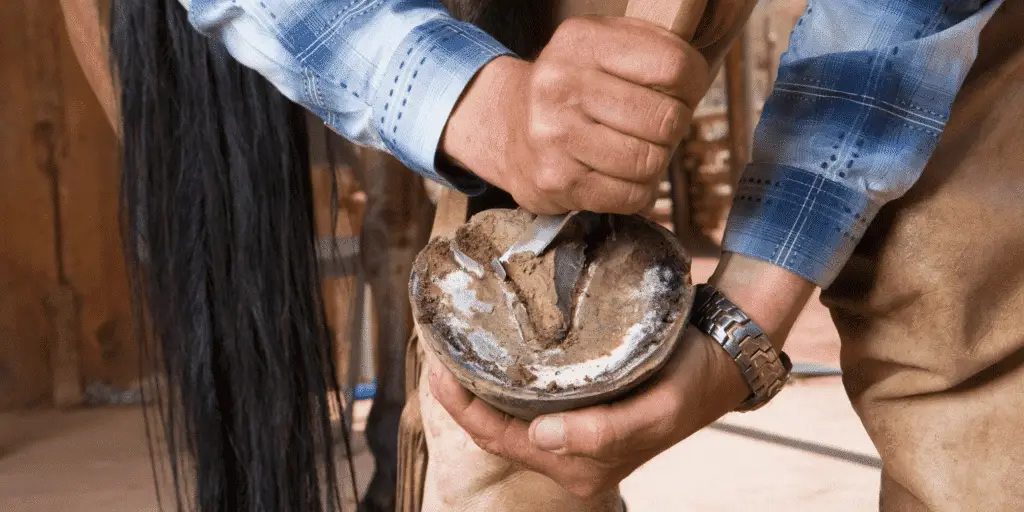
There are enumerous measures that can be taken to prevent ocurrence of Laminitis, including: A diet that provides adequate nutrition based on high-quality forage, digestible fiber (beet pulp) and oil. Avoid excess carbohydrates, especially from grain. Avoid grazing lush pastures, especially between late morning and late afternoon hours, since plant sugars are the highest during these times. Restrict pasture intake during spring or anytime the pasture suddenly greens up. Routine hoof care, including regular trimming.
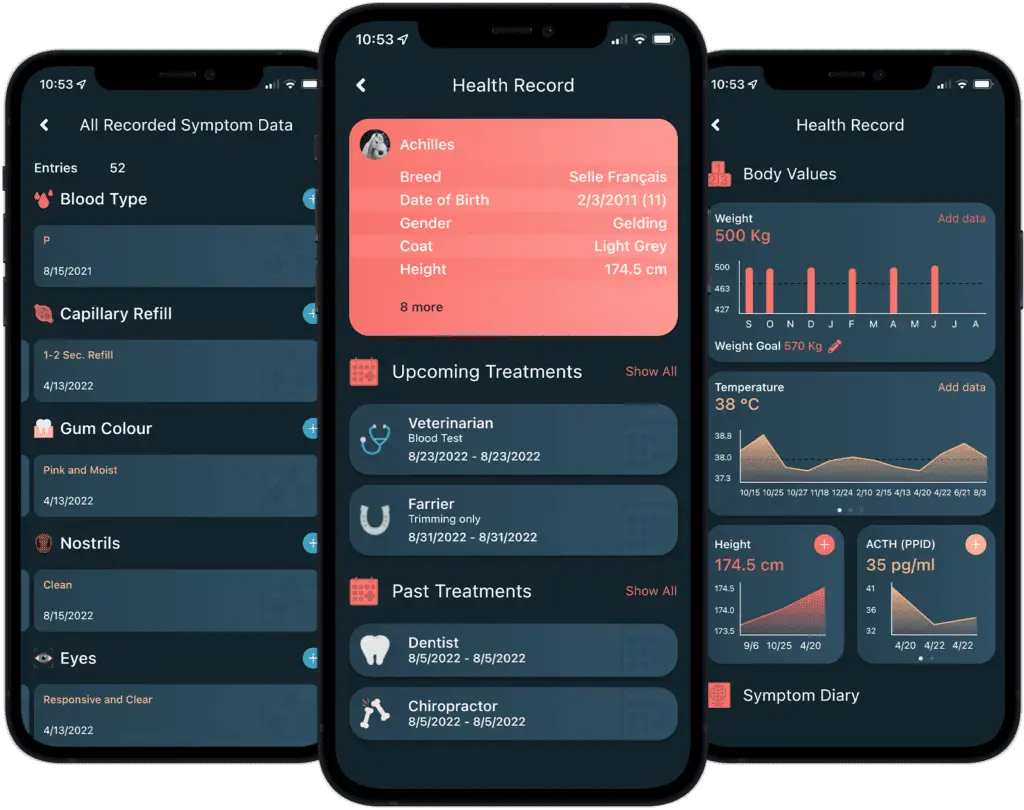
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Sheared Heels in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment. Sheared heels can be defined as a hoof capsule
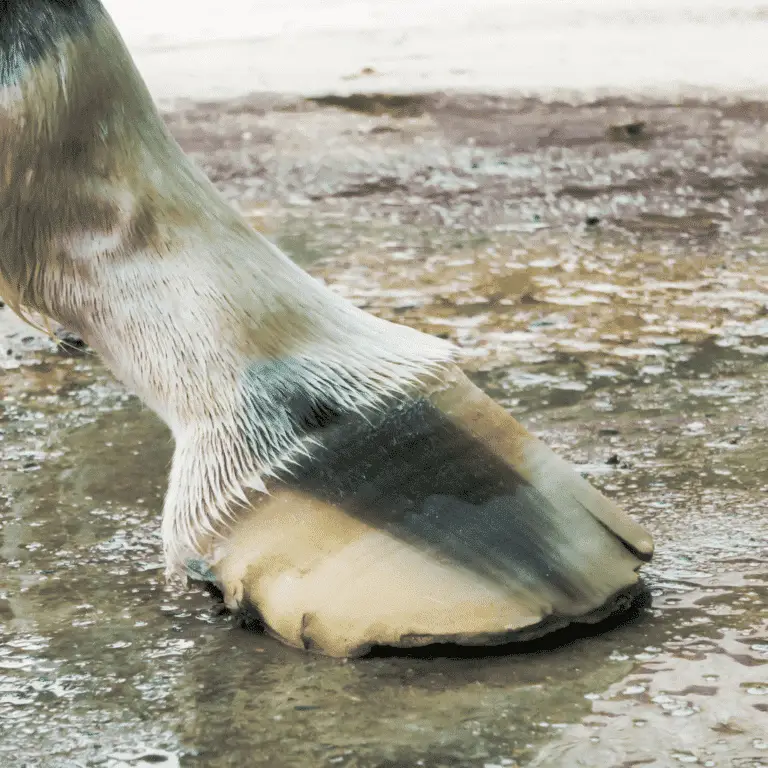

Equine Thrush in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment. Thrush is a common bacterial infection of a hoof’s

Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment.
Coronary sinus quittor in horses is a chronic infection of the collateral cartilages of the hoof, often resulting in abscesses and lameness.