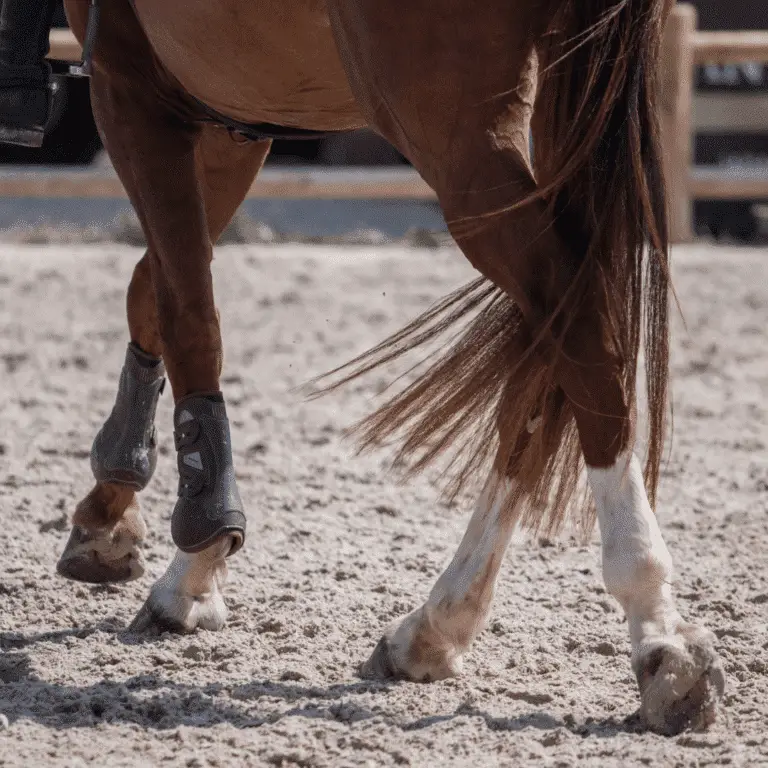

Epiphysitis
Epiphysitis in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Epiphysitis, also known as physitis, is a generalized bone disease of

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
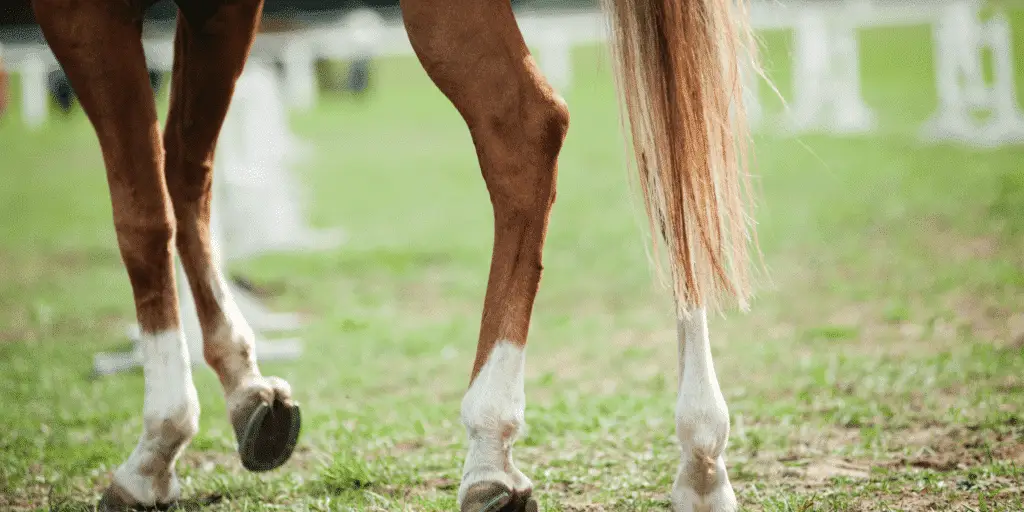
The patella (knee cap) is a mobile structure that glides over the joint surface during locomotion, but can also be locked in position by various ligaments and tendons.
When the horse steps forward, the patella is released from the inside of the medial trochlear ridge, allowing the limb to flex. Problems occur when the patella gets ‘stuck’ in the upward position; this is termed upward fixation of the patella (UFP) or a locking stifle.
In severe cases the leg can remain stuck in extension, however, the condition is often milder and will appear as intermittent hopping as the patella catches and then unlocks during the stride.
For mild locked stifle cases, exercise and a balanced hoof trim may help your horse. Lack of fitness causes weak muscles and ligaments, so simply conditioning your horse can sometimes help solve the stifle problem. For severe locking, ask your farrier to “rocker,” or roll, the toe of the hoof. They can also fit your horse with corrective shoes and pads to help the hoof break over before the locking occurs.
Surgery is usually reserved for very severe cases or those that have not responded well to more conservative and non-invasive treatment options. The most common surgical procedures preformed are the Medial patella ligament desmotomy or Medial patella ligament splitting.
One of the best preventative measures for locking stifle is some simple exercise.
By doing locking stifle exercises with your horse, you can make sure they are not only fit but have a better chance of avoiding the condition altogether.
Many horses who struggle with locking stifle are unfit, and their muscle tone is poor. This is believed to be one of the causes of the condition, so that’s why doing locking stifle exercises is so necessary for prevention.
By keeping a healthy weight, and good fitness routine, horses have less weight bearing down on their joints, better muscle tone, and a better chance their bones will sit adequately together in the stifle joint. All of this equates to fewer instances of locking stifle in horses.
In general, the following tips could help your horse with locking stifle:
Hand-led walks in the pasture for warm-ups, steady, slow backing (backward walking) either on flat surfaces or up a slight incline for more advanced training, riding over low-to the ground poles to encourage leg lifting and muscle development, walk them up hills or slopes, and graduate to trotting as they become used to the exercise.
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Epiphysitis in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Epiphysitis, also known as physitis, is a generalized bone disease of

Poll Evil in Horses This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly. Poll evil is a

Splint Exostoses in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment The most common abnormality is a lumpy splint bone