
Quittor in Horses (Coronary Band Infection)
Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment.
Coronary sinus quittor in horses is a chronic infection of the collateral cartilages of the hoof, often resulting in abscesses and lameness.

Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment.
Fracture of the distal phalanx is a fairly common injury that occurs most commonly at high speed or less commonly from kicking a firm object. The fracture is caused by concussion and produces a sudden onset of lameness. Distal phalangeal fractures occur more frequently in the forelimb but are also common in the hindlimb. Intra-articular fractures may be easily isolated to the foot; lameness is commonly associated with joint effusion.
Nonarticular fractures may require compression of the foot with hoof testers and possibly unilateral palmar digital nerve anaesthesia for localization. Lameness is exacerbated by turning the horse or making it pivot on the affected leg. The clinical signs may be suggestive, but the diagnosis is confirmed by palmar digital nerve block and radiographic imaging.
Treatment options include surgical and nonsurgical therapies. Surgical treatment, whether it is fragment removal or fracture fixation, is primarily used in cases with an articular component where the return of joint congruity in the DIP joint is a major objective of treatment.
Nonsurgical treatment options are often used in combination and include remedial farriery or foot casts in conjunction with box rest/exercise restriction and anti-inflammatory medications. These treatments are also used for post-operative care of cases treated surgically. A bar shoe or foot cast should be considered when a horse with a healed pedal bone fracture is returning to work.
Attention should always be paid to the surfaces over which horses are exercised as hard, concussive going, such as roads, will increase the likelihood of developing fractures.
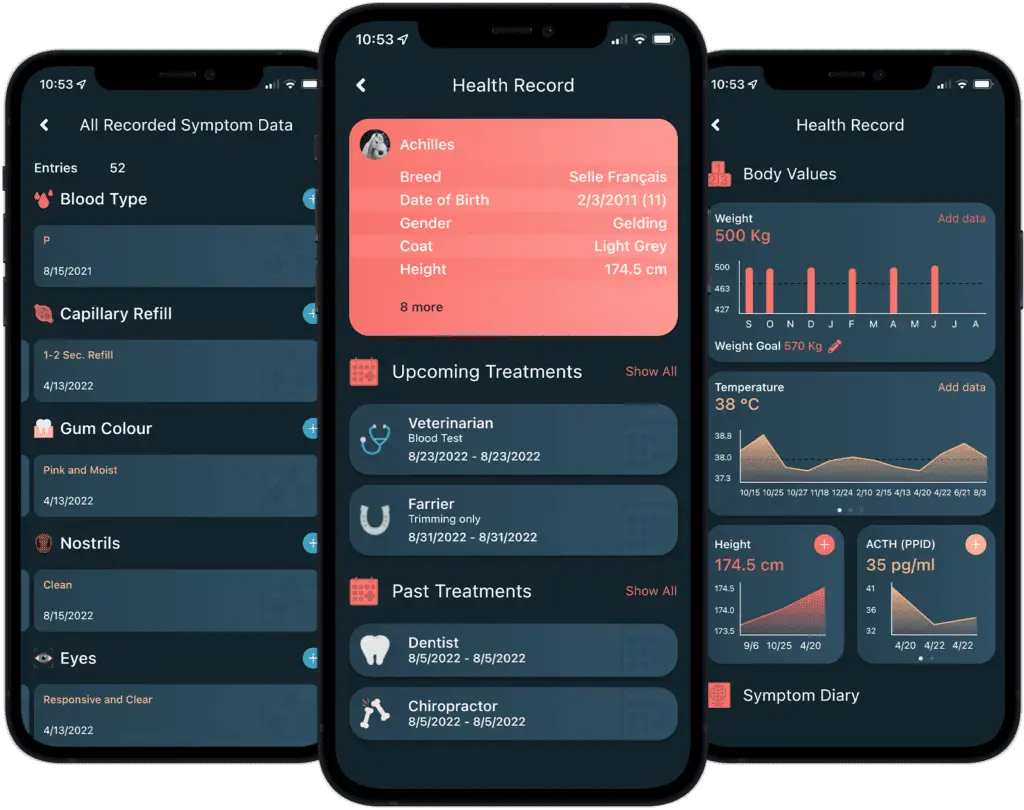
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment.
Coronary sinus quittor in horses is a chronic infection of the collateral cartilages of the hoof, often resulting in abscesses and lameness.

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
Canker is a chronic infection of the hoof characterized by the overgrowth of abnormal tissue in the frog and sole, often with a foul odor.

Heel Bulb Laceration in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment. Lacerations of traumatic origin that occur in the