
Equine Grass Sickness (Equine Dysautonomia)
Equine Grass Sickness (Equine Dysautonomia) This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly. Equine grass sickness

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
Equine strongylosis, a common disease among grazing horses, is caused by infection with a group of nematode parasites known as strongyles. Strongylosis occurs when horses graze on pastures contaminated with strongyle larvae, which hatch from eggs passed in the faeces of infected horses.
Strongyles are classified into two groups: large and small. The large strongyles that infect horses include three Strongylus spp. Small strongyles also known as cyathostomins consist of more than 50 different species from several different genera. Among the large strongyles, S. vulgaris is usually the cause of the most severe disease. Migration of S. vulgaris larvae to the cranial mesenteric artery can cause thrombus formation. Damage to this artery and its branches usually results in interference with blood flow to the intestine and can cause a variety of sequelae.
Adult cyathostomins living in the lumen of the host’s large intestine and cecum cause very little damage. The majority of damage is caused by the larvae during different stages — when they first penetrate the intestinal mucosa and when they emerge from their encysted state.
In general, the approach of strategic deworming and selective treatment is advised. The first should coincide with the times of the year when egg output will be the highest, most commonly in the spring and fall. In the latter each horse in the herd is evaluated with regard to the degree to which it contaminates the pasture; a control program is then developed accordingly.
Regularly rotate pastures. Clean stalls regularly and compost manure. Grouping horses in pastures according to age will help minimize young horses’ exposure to the parasites. New horses being brought into the facility should be dewormed and kept separated from the herd for 72 hours. If an adequate control program has been established, treatment for clinical strongylosis should not be necessary.
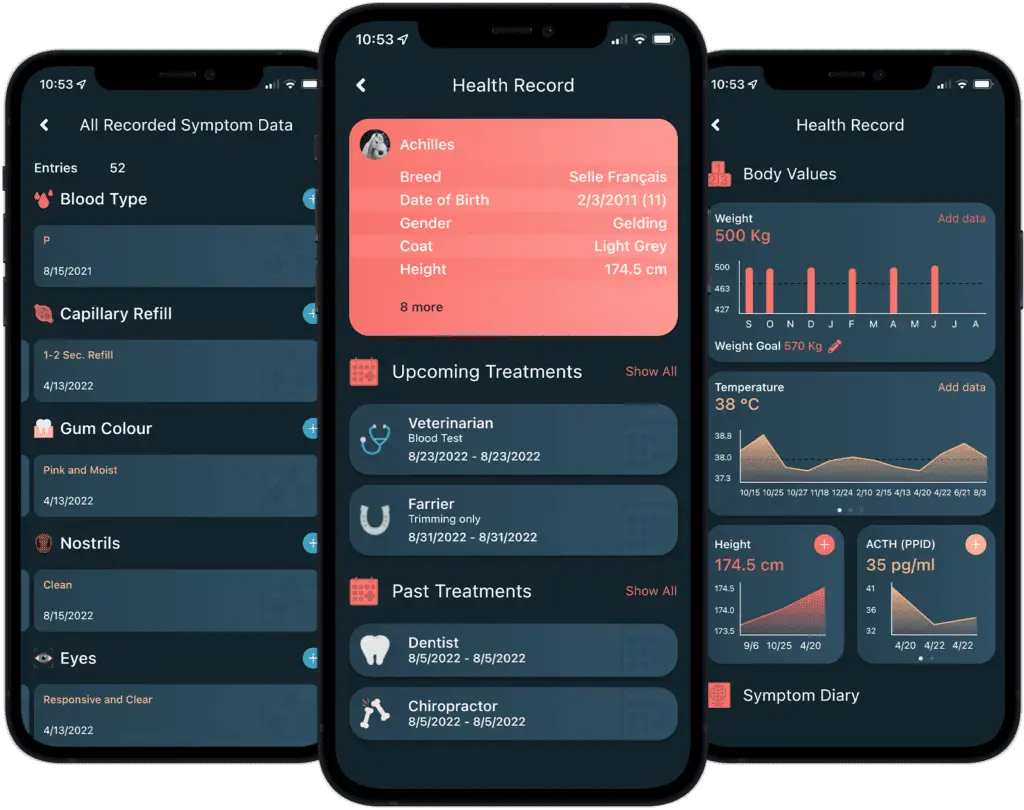
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Equine Grass Sickness (Equine Dysautonomia) This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly. Equine grass sickness

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
Equine motor neurone disease is a progressive neurological disorder in horses causing muscle weakness, weight loss, and trembling.

Borna Disease in Horses This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly. Borna Disease, caused by