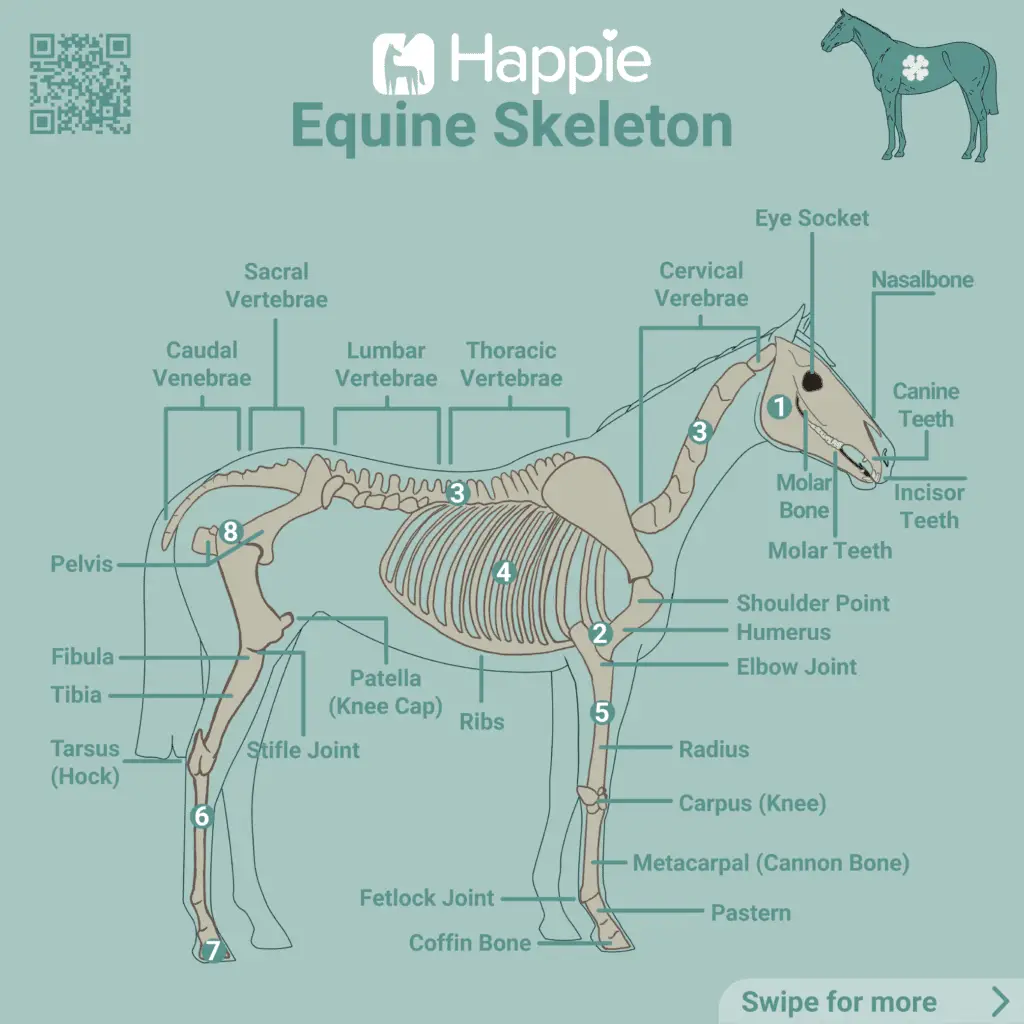
The Skull
The skull is the bone structure that surrounds and protects the brain. It consists of several bones that are intergrown.
The largest bone of the skull is the jaw bone with molars, incisors and the hack teeth. Foals have milk teeth just like humans. From the age of 5 to 6 years, the jaw with all its teeth is fully developed. Then a horse has 36 to 44 teeth (12 incisors, 0-4 stallions or canines, 0-4 wolf teeth and 24 molars).
A horse’s head can weigh up to 30 kilograms. Together with bones, muscles etc., the head and neck take up to one third of the total weight.
The Sternum
The sternum, also called the breastbone, is located in the chest region. It stabilises and at the same time provides flexibility and mobility for breathing.
It is positioned on the inside of the shoulder blade and extends to the last neck spine and ribs.
The Spine
The spine consists of several vertebrae and extends from the skull to the tail, thus covering almost the entire horse body. It provides support, flexibility and at the same time protects the spinal cord.
The spine is divided into 7 neck vertebrae, 18 back vertebrae, 5 to 7 lumbar vertebrae, 5 sacral vertebrae and 21 tail vertebrae. In total, a horse has 56-58 vertebrae.
The Ribs
The ribs surround the rib cage and protect vital organs, such as the heart and lungs. Horses have between 17 and 18 pairs of ribs. Of these pairs of ribs, 8 are fixed ribs, which are firmly attached to the sternum. The other ribs are movable respiratory ribs for breathing.
The Front Limbs
The front limbs carry the majority of the weight (approx. 60-65%) and consist of the shoulder blade, carpal joint, forearm bones, pastern bones and hooves.
The Hind Limbs
The hind limbs consist of the pelvis, tibia and fibula, hock joint, tubular bone, pastern bone and hoof.
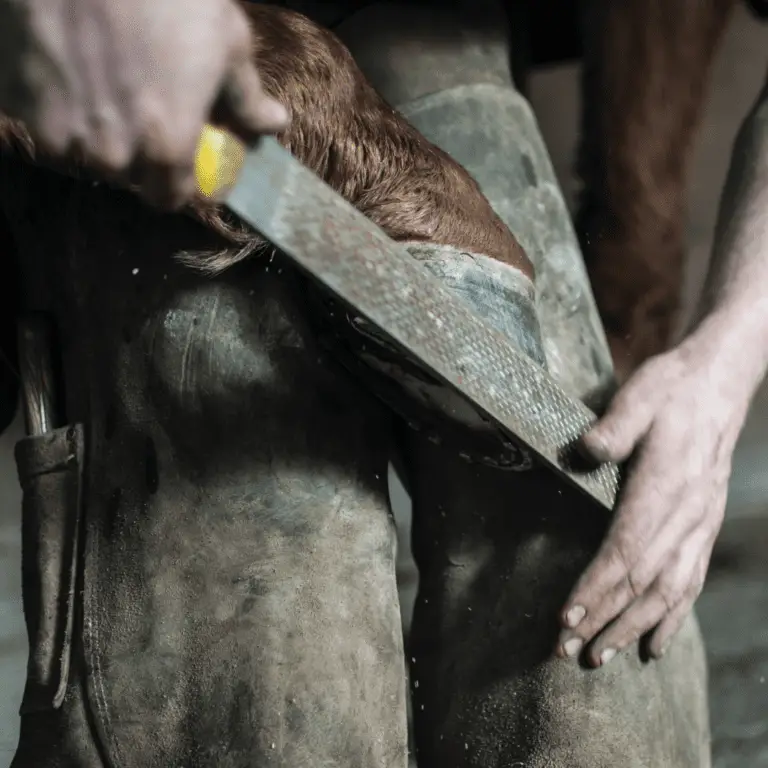
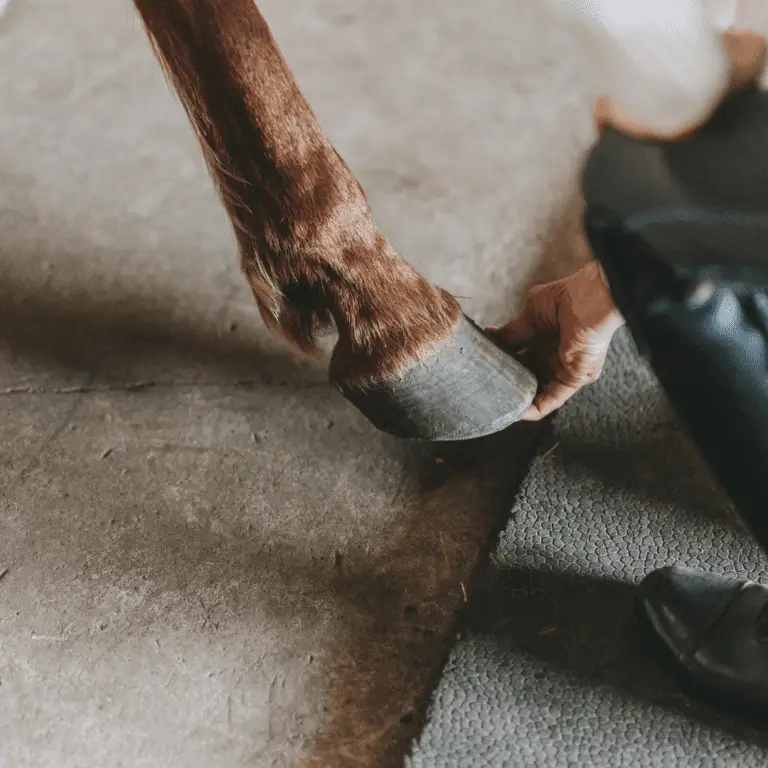
The Hoof
From the anatomical perspective, the hoof is a horse’s fingernail. The hoof is made of keratin and is composed of the hoof wall, pads, sole and frog. Wild horses wear down their hooves evenly. The hoof of a domestic horse, on the other hand, needs to be treated by a farrier every 6-8 weeks, as wearing and regrowth of the hoof are out of balance.
The Horse Pelvis
The pelvis, also called the pelvic cavity, supports stability, mobility and power transmission of the hind limbs. This is also the largest bone in the horse.