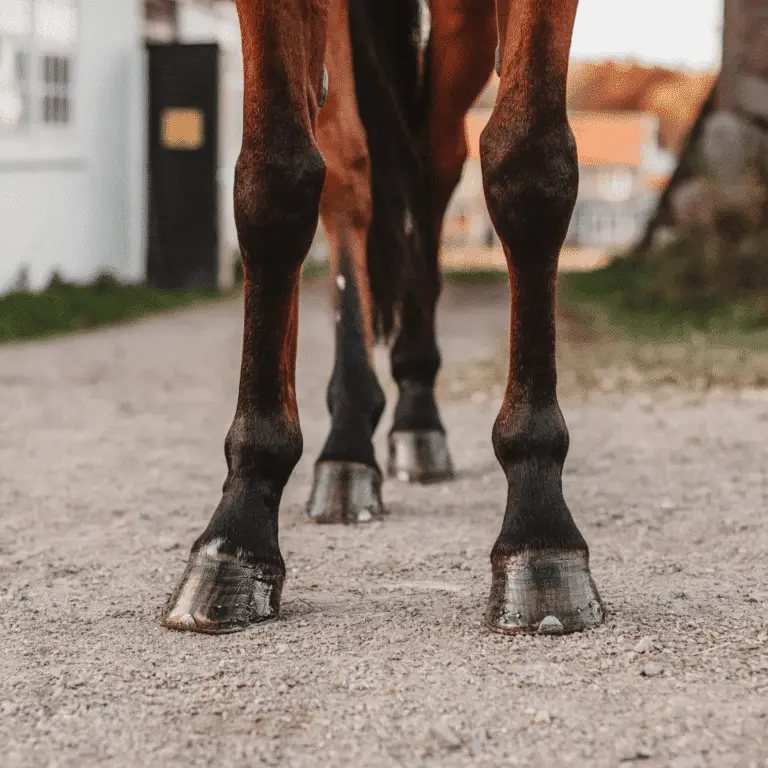

Pedal Bone Fracture in Horses
Pedal Bone Fracture in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment. Fracture of the distal phalanx is a fairly

Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment.
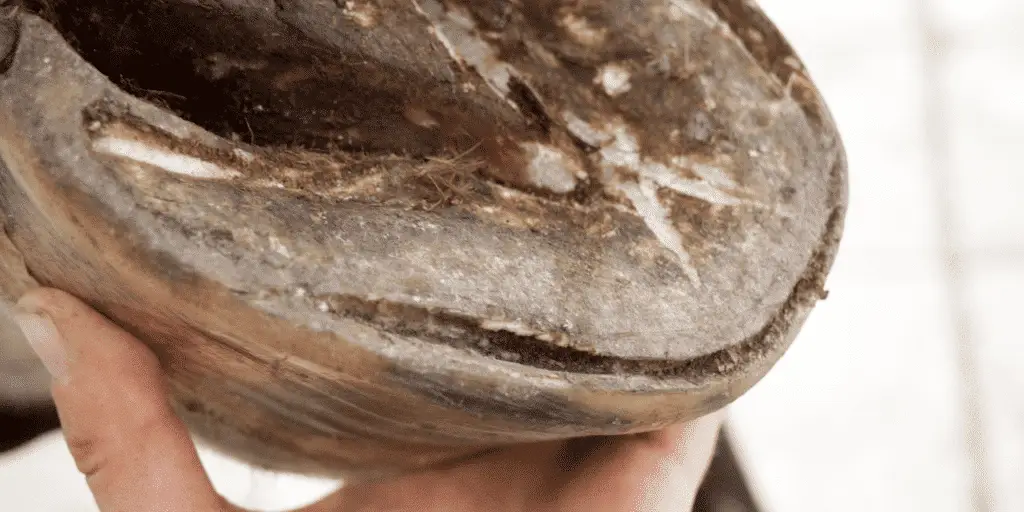
White Line Disease is caused by the invasion of fungi or bacteria which attacks the hoof-wall tissue, causing it to separate from the sole at the white line of the hoof.
These fungi and bacteria can only enter when there is a separation due to a deformation of the hoof, an imbalance in the hoof’s moisture due to extreme moisture or dryness, trauma or lamintis.
Therapy of white line disease is directed at protecting and unloading the damaged section of the foot with therapeutic shoeing combined with resectioning the hoof capsule that overlays the affected area. The debridement should be continued proximally and marginally until there is a solid attachment between the hoof wall and external lamellae.
Treatment with topical medications after hoof wall resection is done with disinfectants/astringents such as methiolate or 2% iodine. These act as a good disinfectant but may have more benefits as a dye marker to outline the remaining tracts. The above preparations should be applied at most twice weekly to make the exposed laminae manageable. Thorough exploration and debridement of any remaining tracts should take place at 2-week intervals.
Regular trimming can prevent White Line Disease. Another factor that should be considered is adequate nutrition in the horse’s diet.
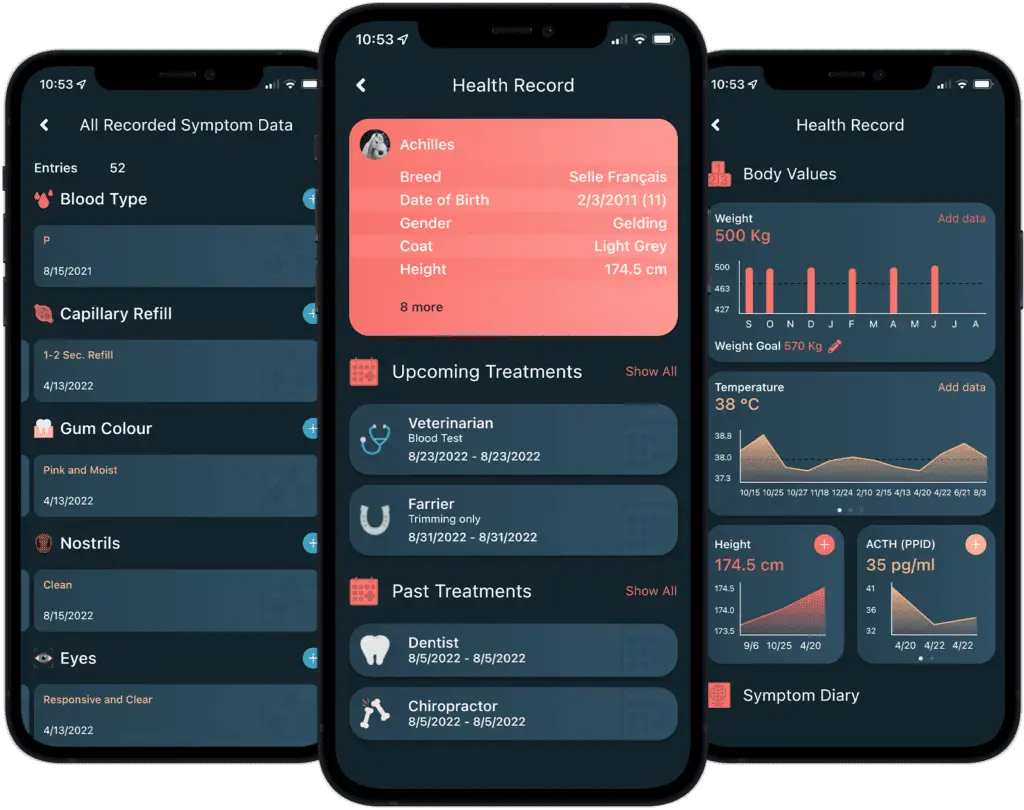
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Pedal Bone Fracture in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment. Fracture of the distal phalanx is a fairly

Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment.
Coronary sinus quittor in horses is a chronic infection of the collateral cartilages of the hoof, often resulting in abscesses and lameness.
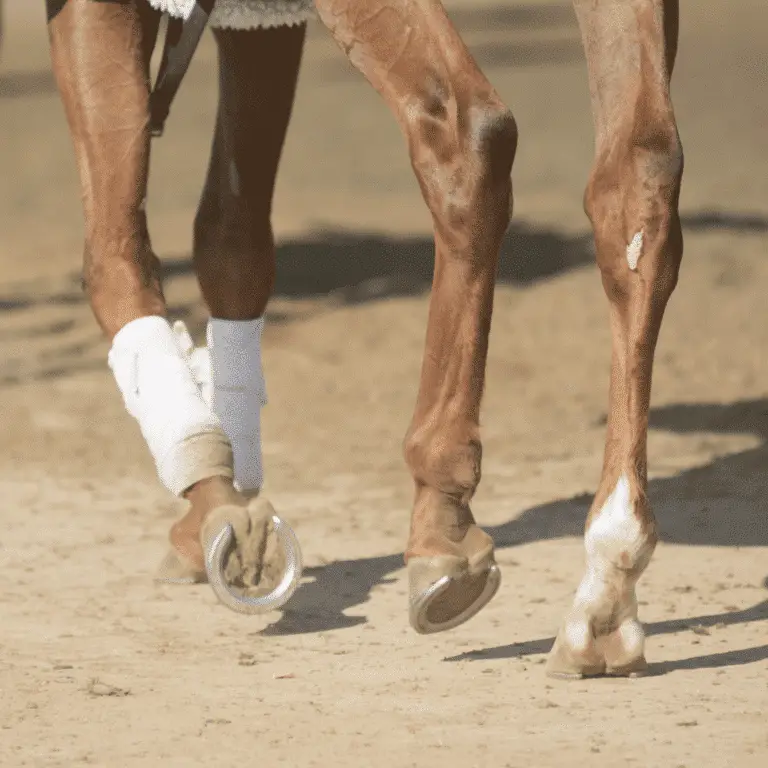

Heel Bulb Laceration in Horses Seek veterinary advice before applying any treatment. Lacerations of traumatic origin that occur in the