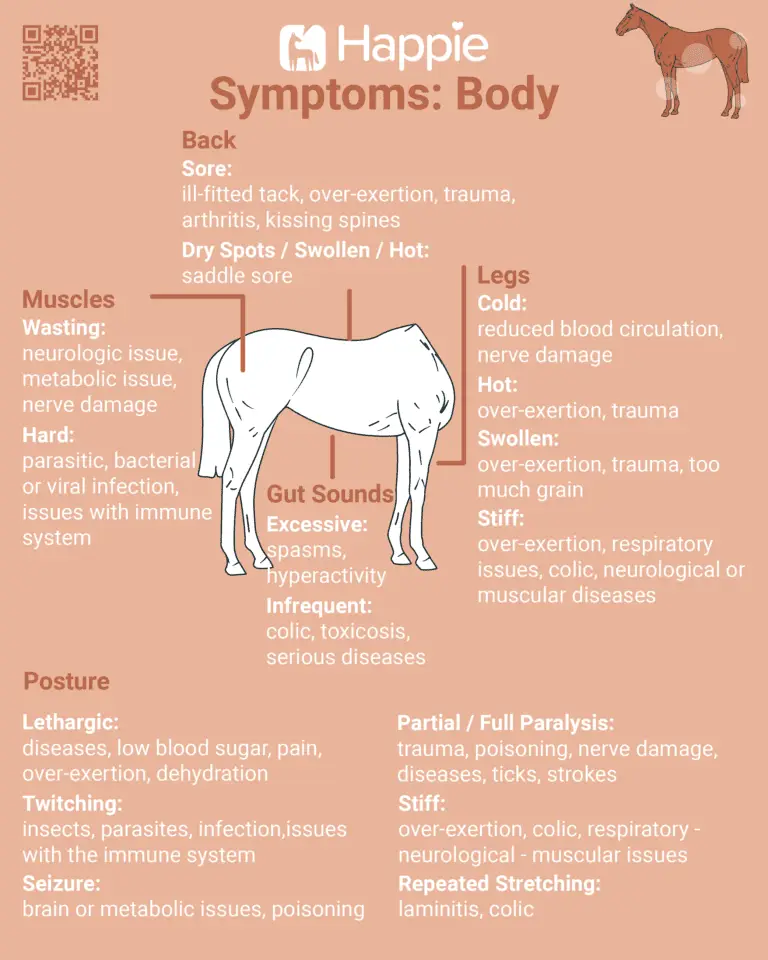
The posture of your horse is a good indicator of possible health problems.
Look for lethargy, frequent twitching, stretching, cramping, partial or full paralysis or stiffness.
Lethargy is a sign of disease, low blood sugar, overwork or dehydration.
Horses that often twitch may also be infested with insects or parasites, or suffer from infection or an immune disorder, among other things.
Brain disorders, metabolic disorders or poisoning are often accompanied by seizures.
If your horse is affected by partial or total paralysis, then an examination for tick bites, trauma, poisoning, nerve damage, strokes or other diseases is recommended.
Repeated stretching is a symptom of colic or laminitis.
Save this chart with all the symptoms and keep track of your horse’s health: