
Equine Sarcoids
Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
Equine sarcoids are common skin tumors in horses caused by the bovine papillomavirus, often presenting as locally invasive growths.

This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly.
Treatment options are determined by the size and location of the tumour. Smaller lesions are generally easier to treat. Unfortunately, many tumours are large by the time they are noticed, especially if they are located on the third eyelid, which can be difficult to see.
Surgery combined with follow-up treatment is the best option in many cases.
If the tumour can’t be surgically removed (it’s in a difficult place, for example), chemotherapy may be an option. The growths can be injected with a cytotoxic (cell-killing) drug such as cisplatin. Those around the sheath can be treated with a topical drug.
Squamous cell carcinoma also can be treated with radiation. In one method, radioactive “seeds” are implanted in the tumour and left in place for a few days to destroy the abnormal tissue.
Cryotherapy (freezing) is sometimes used for small external growths.
Limiting exposure to ultraviolet radiation may help prevent squamous cell carcinomas, especially in horses with white or partially white coats.
Give horses with pink skin on the face or other areas extra protection from the sun, like fly masks. Turn them out at night and keep the horse stabled during hours of peak sunlight.
Clean a gelding’s sheath regularly; there’s some thought that a buildup of dirt and smegma contributes to cancer there.
Check light-skinned areas regularly and thoroughly to catch this cancer while it’s treatable.
Owners can use DNA testing to identify horses that are at higher risk for ocular SCC development and take precautions to protect them.
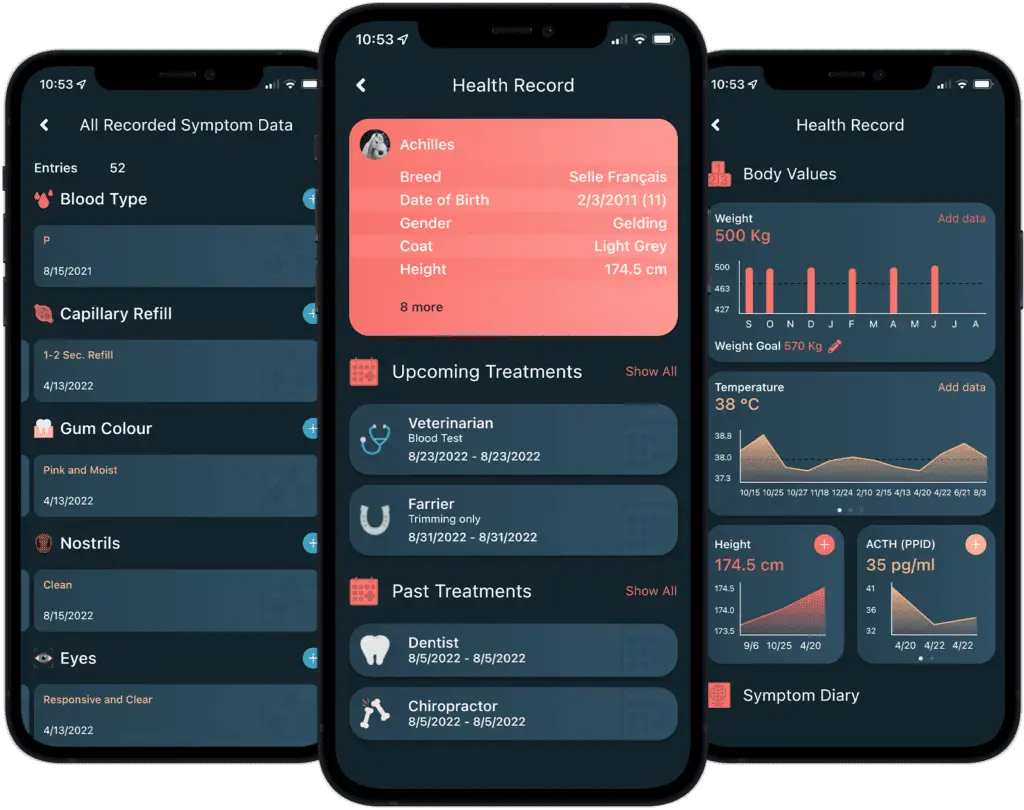
Digital health management offers numerous benefits in modern equine healthcare.
With the Happie Horse App, you can track symptom patterns and body values, such as Temperature, Pulse and Respiration. Allowing you to notice abnormal changes in body and behaviour early on, leading to more successful treatments.
The Happie symptom checker allows you to add all of your horse’s abnormal symptoms in order to present potential causes and diseases.

Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease.
Equine sarcoids are common skin tumors in horses caused by the bovine papillomavirus, often presenting as locally invasive growths.

Equine Melanoma in Horses Seek veterinary advice if you suspect this disease. Melanomas are cancerous growths most commonly associated with

This disease is life-threatening and should be treated by a veterinarian swiftly.
Equine lymphoma is a cancer affecting the lymphatic system in horses, often marked by enlarged lymph nodes and diverse symptoms.